Troubleshoot LED Light Issues

Ever wonder why your LED lights act up? You might notice dimness, flickering, or weird colors. Most problems come from things like poor heat sinks, low-quality LEDs, or voltage drops. Don’t worry—when you troubleshoot LED light issues, you can often fix them fast. Start by spotting your exact problem.
Key Takeaways
Look for loose connections and make sure bulbs are tight. This easy step can stop lights from flickering or being dim.
Always use an LED driver that fits your bulb’s needs. The wrong driver can cause problems and make your lights not last as long.
Check and clean your LED lights often to get rid of dust and dirt. This helps your lights stay bright and work well.
Common Problems With LED Lighting

You might see problems with led lighting a lot. Let’s look at what can go wrong and why it happens.
LED Light Flickering
Flickering lights can be really annoying. Sometimes your led lights flash or pulse. This happens when you turn them on or try to dim them. About 23% of bulbs flicker a lot. Around 32% flicker sometimes. Only 45% do not flicker at all.
Flicker Category | Percentage of LED Bulbs |
|---|---|
Completely Flicker-Free | 45% |
Very High Flicker | 23% |
Intermediate Flicker | 32% |
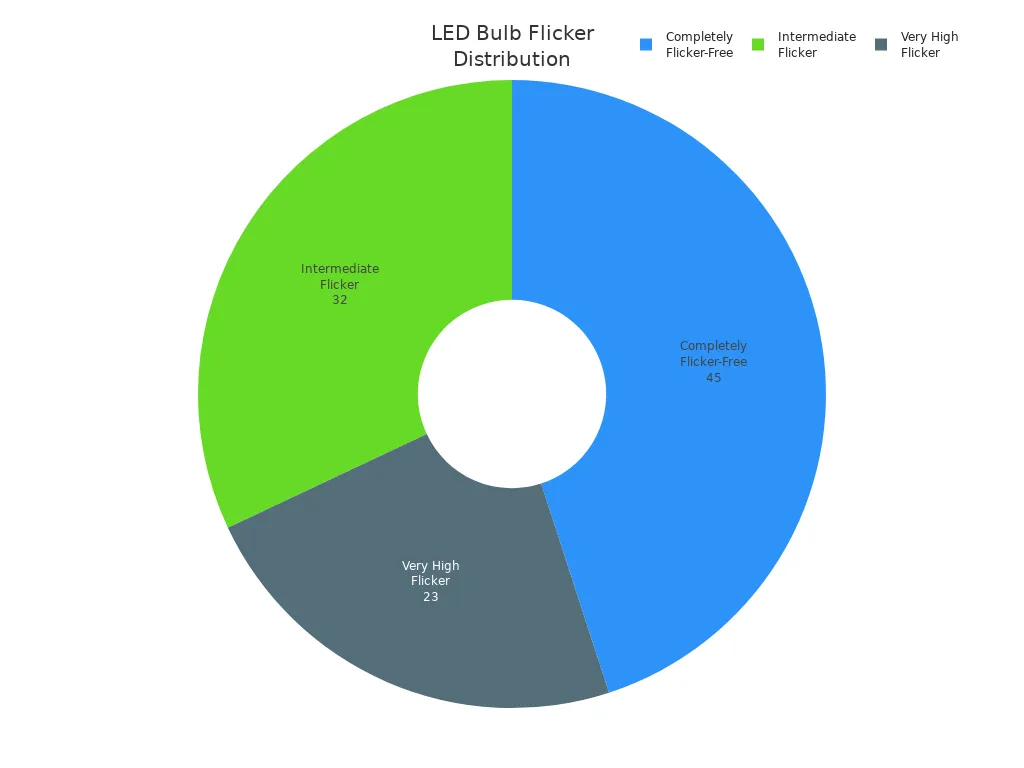
You might see flickering because wires are loose. Bad drivers or dimmer switches that do not match can cause it too. Sometimes, voltage drops or big appliances turning on and off make led lights flicker.
Buzzing Sounds
Buzzing from lights can get annoying quickly. You might hear buzzing if you use the wrong dimmer. Poor driver circuits can also make buzzing sounds. Electromagnetic interference and cheap parts can cause buzzing too.
Dim or Low Brightness
Dim lights make rooms look boring. Led bulbs can get dim if they get old. Controls that do not match how you see light can cause dimness. Old wiring or fixtures that do not match can make lights dim.
Color Issues
Color problems show up as strange shades or colors that change. Led lighting can change color if materials are bad or installation is poor. Mixing old and new bulbs can cause color shift.
Color stability is different for each product and brand, so you should check this in the product details. Color shift can change the light’s CCT and CRI a lot over time.
Overheating
Overheating can hurt your led lighting. Bad thermal management or closed fixtures can cause overheating. Using too much power through your led bulbs can also make them too hot. Overheating can make your lights not last as long and can be unsafe.
If you notice these problems with led lighting, you are not alone. Most people deal with flickering, buzzing, dim lights, color problems, or overheating sometimes. Knowing what causes these problems helps you fix them and make your lights work better.
Troubleshoot LED Light Issues
When you troubleshoot led light issues, you want to start with the basics. Most problems come from loose electrical connections, using the wrong led driver, or a voltage drop affecting performance. Let’s walk through each step so you can fix your lights fast.
Check Bulb and Connections
Loose electrical connections can make your LED lights flicker, buzz, or go dim. You might even see them turn off completely. Here’s how you can check your bulbs and connections safely:
Turn off the power before you touch anything. This keeps you safe from electric shock.
Put on insulated gloves and safety glasses. You want to protect your hands and eyes.
Avoid touching exposed wires or metal parts. These can carry electricity.
Use the right tools. A multimeter helps you test voltage, and a lux meter checks brightness.
Test your LED bulb with a battery. Find the bulb’s terminals, connect them to a battery, and see if it lights up. If it doesn’t, the bulb might be bad.
Tip: If you notice flickering or dimming, tighten the bulb in its socket. Sometimes, a loose electrical connection is the only problem.
Loose electrical connections can also happen inside the fixture. If you see wires that look frayed or discolored, you should fix them. Using the wrong led driver can also cause problems. Make sure the driver matches your bulb’s needs.
Inspect Power Supply
The power supply is the heart of your LED system. If you use the wrong led driver or have a voltage drop affecting performance, your lights won’t work right. Here’s what you should check:
Verify the voltage. The power supply voltage must match your LED’s rated voltage. If it’s too low or too high, you’ll see dim lights or even damage.
Assess the power supply’s capacity. Add up the total power your LED strips or bulbs need. Make sure your power supply can handle it.
Here’s a table to help you spot common power supply issues:
Issue | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
Sudden Brightness Drop | Problems with power supply, overheating, or failing components. | Inspect power supply for stable voltage. |
Flickering Lights | Voltage fluctuations, incompatible dimmer switch, loose electrical connections, or faulty driver. | Check voltage, dimmer compatibility, wiring, and replace driver. |
Dim Lights | Weak power supply, aging LEDs, or overheating. | Ensure enough voltage, check LED age, improve ventilation. |
Light Not Turning On | Blown fuse, faulty wiring, defective driver, or dead LEDs. | Check fuse, wiring, driver, and replace dead LEDs. |
If you notice a voltage drop affecting performance, you might need a stronger driver or better wiring. Using the wrong led driver can make your lights flicker or go dim. Always match the driver to your LED’s specs.
Test Switches and Dimmers
Switches and dimmers control your LED lights. If you use an incompatible dimmer switch, you’ll see flickering, buzzing, or even overheating. Here’s how you can troubleshoot led lights with switches and dimmers:
Check bulb compatibility. Make sure your dimmer switch works with LED bulbs. Old dimmers often don’t match.
Look at the installation. A poorly installed dimmer can cause problems.
Test and replace the switch if needed. If you still see issues, try a newer dimmer model.
Note: Incompatible dimmers can cause flickering, buzzing, and reduce the dimming range. They can even make your bulbs overheat or fail early.
Using the wrong led driver with your dimmer can also cause trouble. If your lights buzz or flicker, check both the driver and the dimmer switch. Loose electrical connections at the switch can also lead to problems.
Examine Wiring and Corrosion
Bad wiring and corrosion can ruin your LED lighting. You might see flickering, dimming, or lights that won’t turn on. Here’s what to look for:
Inspect receptacles for corrosion. Rust or green spots mean trouble.
Check connections for accidental cross-wiring. Wires in the wrong place can stop your lights from working.
Identify poor wiring by looking for discoloration or frayed wires.
Watch for flickering or dimming. These are signs of loose electrical connections or using the wrong led driver.
To troubleshoot led light issues caused by wiring or corrosion, follow these steps:
Schedule regular inspections. Catch problems before they get worse.
Check for loose connections and signs of corrosion. Fix them right away.
Monitor for overheating. Touch your LED lights to see if they feel too hot.
Clean dust and debris. This keeps your lights bright.
Make sure wires connect with the right polarity. Wrong connections can cause malfunction.
Test the power supply and connections for tightness and corrosion.
Inspect LED chips for damage. Replace any that look burned or broken.
Tip: If you see flickering or dimming, check for loose electrical connections first. Many problems start there.
Using the wrong led driver or having a voltage drop affecting performance can make wiring problems worse. Drivers need good wiring to work right. If you troubleshoot led lights regularly, you’ll catch these issues early.
When you troubleshoot led light issues, always start with the basics. Check your bulbs, connections, power supply, switches, dimmers, and wiring. Most problems come from loose electrical connections, using the wrong led driver, or a voltage drop affecting performance. Fix these, and your LED lights will shine bright again.
Troubleshoot LED Lights in Fixtures and Strips

Fixture Compatibility
When you install LED bulbs in fixtures, you want everything to fit and work right. Sometimes, you run into problems because the fixture and bulb don’t match. Here are some things you should check:
Socket type and size must match the bulb.
Wattage rating of the fixture should fit the LED bulb.
Lumen output needs to give you enough brightness.
You might need to change the socket or remove a ballast for some fixtures.
Old fixtures may not work well with new LED technology.
Warranty coverage can disappoint you if the fixture fails early.
You can use this table to help you spot what matters most:
Consideration | Description |
|---|---|
Fixture Type | Make sure your fixture supports LED bulbs. |
Base Type | Match the bulb base (like E26 or GU10) to the fixture. |
Wattage | Check the wattage for proper brightness. |
Voltage | The bulb’s voltage must fit the fixture. |
Dimmer Compatibility | Use dimmable bulbs with the right dimmer switch. |
Thermal Management | Good heat flow keeps your LED bulb working longer. |
LED Strip Power Ratings
LED strips need the right power to shine bright and last long. If you use the wrong power rating, the strips can overheat and burn out fast. High drive currents make LEDs brighter but also hotter. Too much voltage can cause safety problems and shorten the life of your strips.
Here’s a quick look at common LED strip power ratings:
LED Strip Type | Idle Power Consumption | Full Brightness Power Consumption |
|---|---|---|
WS2811 | 1.27 watts | 19.68 watts |
WS2812B | Half of WS2811 | 13.6 watts |
WS2815 | 3.52 watts | 20.18 watts per 150 LEDs |
SK6812 | 0.83 watts | 10 watts |
Smart LED Integration
Smart LED lights can make your home feel modern. You might face challenges when you connect them to your smart hub. Sometimes, you see inconsistent color temperature or brightness. Compatibility between your lights and hub matters a lot. Firmware updates help your devices work better. Automation rules can cause problems if you set them wrong.
Tip: Start with pre-set scenes and adjust them to fit your style. Always check if your smart lights work with your app or assistant.
If you run into trouble, try resetting your device and keeping it close to the hub. Community forums can help you find answers from other users.
Preventing LED Light Issues
Proper Installation
You want your LED lights to work well right away. Most problems happen if you install them wrong. Flickering or lights not turning on are common issues. If you connect the power source the wrong way, your LEDs might not work. Loose wires can make your lights fail. Long wires can cause voltage drops and dim lights. Using the wrong driver also causes trouble. Here is a table that shows common mistakes:
Installation Error | Description |
|---|---|
Incorrect power source connection | Not connecting the fixture right can cause problems. |
Loose electrical connections | Flickering or lights not working can happen. |
Voltage drop issues | Long wires can make lights dim or flicker. |
Incorrect LED driver | A driver that does not match can cause issues. |
Tip: Always check your wiring and driver before you finish. If you install things wrong, your lights may not last as long.
Heat Management
LEDs can get hot if you do not manage heat well. Bad installation can block airflow and trap heat. You can use heat sinks, vents, or flexible PCBs to keep LEDs cool. Here are some smart ways to manage heat:
Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
Modular Heatsink Assembly | Keeps cooling and light parts separate for better results. |
Integrated Heat Transfer Panel | Uses heat sinks and vents to help LEDs last longer. |
Snap-Fit Cylindrical Heat Sink | Lets air move and helps heat go away. |
Flexible PCB for Heat Dissipation | Moves heat straight to the air. |
Passive Ventilation Structure | Makes air flow without using fans. |
If your LEDs feel hot, check for blocked vents or crowded fixtures. Good heat management helps your lights last longer.
Regular Maintenance
Taking care of your LED lights helps them work longer. Dust and loose wires can cause problems if you ignore them. Clean your lights often and tighten any loose wires. Make sure your lights have enough air flow. Watch the room temperature and follow the instructions from the maker. Here is a table that shows what helps:
Maintenance Practice | Impact on Longevity and Performance |
|---|---|
Regular Cleaning | Removes dust and helps lights shine brighter and last longer. |
Inspect and Tighten Connections | Stops flickering and keeps lights working. |
Maintain Adequate Ventilation | Stops heat from building up and keeps LEDs working well. |
Monitor Ambient Temperature | Helps your LEDs last longer. |
Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines | Makes sure you care for your product the right way. |
Schedule Professional Inspections | Finds problems early and keeps your system working. |
You do not need fancy tools. A soft cloth, a screwdriver, and some care help you avoid problems from bad installation and keep your LEDs bright.
You can spot the cause of premature failure in your LED lights by checking each issue. If you follow these steps, you avoid premature failure of energy-efficient bulbs. You fix problems fast and keep your lights bright. Don’t let premature failure of energy-efficient bulbs stop you. You’ve got this!
FAQ
Why do my LED lights flicker sometimes?
Loose connections or the wrong dimmer can cause flickering. Try tightening the bulb or switching to a compatible dimmer.
Tip: Check your wiring first. Flickering often starts there.
Can I use any LED bulb in my old fixture?
Not always. You need to match the base type and wattage. Some old fixtures need a new socket or driver.
Always check the fixture label before installing.
What should I do if my LED lights feel hot?
Turn off the lights and let them cool. Check for blocked vents or crowded fixtures. Good airflow helps your LEDs stay safe.
See Also
Exploring LED, RGB, And Battery Options For Acrylic Displays
Selecting The Ideal Wall-Mounted Display For LED Light Boxes
Types, Uses, And Setup Of Acrylic LED Light Boxes

